Below, we’ll explore what exactly goes on a balance sheet. Balance sheets are typically prepared and distributed monthly or quarterly depending on the governing laws and company policies. Additionally, the balance sheet may be prepared according to GAAP or IFRS standards based on the region in which the company is located. If we rearrange the Accounting Equation, Equity is equal to Assets minus Liabilities. Net Assets is the term used to describe Assets minus Liabilities.
How does the Accounting Equation work?
This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced. That is, each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry (or coverage) on the credit side. This account includes the total amount of long-term debt (excluding the current portion, if that account is present under current liabilities).
What Is Shareholders’ Equity in the Accounting Equation?
You can think of them as resources that a business controls due to past transactions or events. To make the Accounting Equation topic even easier to understand, we created a collection of premium materials called AccountingCoach PRO. Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way.
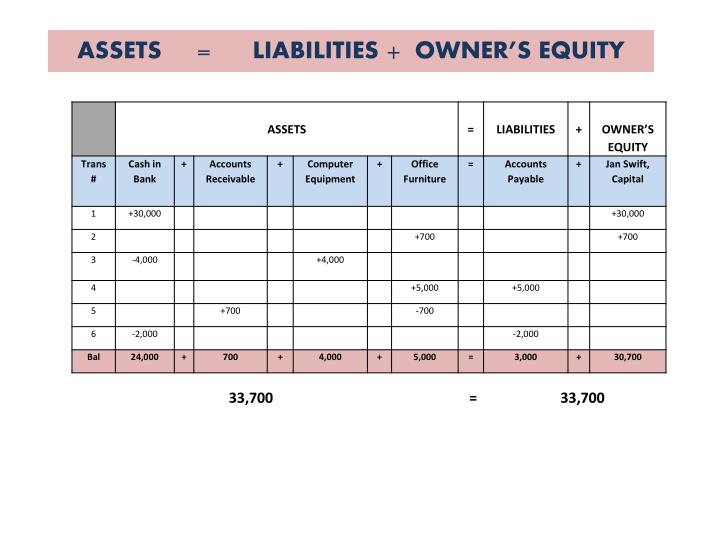
Assets = Liabilities + Equity

The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity. For example, if the total liabilities of a business are $50K and the owner’s equity is $30K, then the total assets must equal $80K ($50K + $30K). The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. This financial statement lists everything a company owns and all of its debt. A company will be able to quickly assess whether it has borrowed too much money, whether the assets it owns are not liquid enough, or whether it has enough cash on hand to meet current demands. It’s commonly held that accounting is the language of business.
Depending on the company, different parties may be responsible for preparing the balance sheet. For small privately-held businesses, the balance sheet might be prepared by the owner or by a company bookkeeper. For mid-size private firms, they might be prepared internally and then looked over by an external accountant. We also allow you to split your payment across 2 separate credit card transactions or send a payment link email to another person on your behalf.
- This equation sets the foundation of double-entry accounting, also known as double-entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet.
- Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid.
- The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet.
- Depreciation of an asset can be allocated variably, depending on the point of view of the person assessing the asset.
The term capital includes the capital introduced by the business owner plus or minus any profits or losses made by the business. Profits retained in the business will increase capital and losses will decrease capital. The accounting equation will always balance because the dual aspect of accounting for income and expenses will result in equal increases or decreases to assets or liabilities. The assets on the balance sheet consist of what a company owns or will receive in the future and which are measurable. Liabilities are what a company owes, such as taxes, payables, salaries, and debt. The shareholders’ equity section displays the company’s retained earnings and the capital that has been contributed by shareholders.
Explore our online finance and accounting courses, which can teach you the key financial concepts you need to understand business performance and potential. To get a jumpstart on building your financial literacy, download our free Financial Terms Cheat Sheet. If this balance sheet were from a US company, it would adhere to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), and the order of accounts would be reversed (most liquid to least liquid). Owners’ equity, also known as shareholders’ equity, typically refers to anything that belongs to the owners of a business after any liabilities are accounted for. Just as assets are categorized as current or noncurrent, liabilities are categorized as current liabilities or noncurrent liabilities. It’s important to remember that a balance sheet communicates information as of a specific date.
This information is not a recommendation to buy, hold, or sell an investment or financial product, or take any action. This information is neither individualized nor a research report, and must not serve as the basis for any investment decision. All investments involve risk, including the possible loss what is a sales invoice complete guide on how to create one of capital. Past performance does not guarantee future results or returns. Before making decisions with legal, tax, or accounting effects, you should consult appropriate professionals. Information is from sources deemed reliable on the date of publication, but Robinhood does not guarantee its accuracy.